3 Key Distinctions of Air Ducts vs. Vents
In the intricate world of home heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, the terms “air ducts” and “air vents” are frequently mentioned. These components are fundamental to the functionality of your HVAC system, yet they are often misunderstood or not differentiated properly. While they work in tandem to regulate and maintain the climate within your indoor environment, their roles and operations are distinctly different.
Understanding these differences is not just a matter of technicality or semantics—it’s crucial for any homeowner interested in optimizing their home’s energy efficiency, improving air quality, and ensuring the overall longevity of their HVAC system. Proper knowledge of how air ducts and air vents function can also empower you to make informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, or when troubleshooting issues.
Air ducts can be likened to the veins and arteries of your HVAC system, hidden beneath the surfaces of your home, silently and efficiently carrying air to and from your living spaces. On the other hand, air vents are the more visible elements that deliver the conditioned air into each room, allowing you to control and direct the flow of air where it is most needed. Together, these components ensure that your home maintains a comfortable and healthy environment.
In this blog post, we will delve into the specific roles and functions of air ducts and air vents. We’ll explore their design, the materials used to construct them, and their critical contributions to the HVAC system’s overall function. Additionally, we will provide insight into the best practices for maintaining these components to help maximize your system’s efficiency and improve the quality of air throughout your home.
By understanding the key differences and how to effectively manage these essential parts of your HVAC system, you can enhance your home’s comfort and potentially reduce your energy costs. Let’s embark on this journey to uncover the hidden lifelines of your HVAC system and learn how to keep them functioning at their best.
What are Air Ducts?
Air ducts are essential components of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. They function as the circulatory system of your home or building, designed to distribute air efficiently throughout the space. Here are the key aspects of air ducts:
Structure and Material
Air ducts are typically constructed from a variety of materials including sheet metal, fiberglass, or a flexible plastic and wire composite. The choice of material often depends on the specific requirements of the building and the HVAC system design. Metal ducts, particularly those made from galvanized steel or aluminum, are durable and less susceptible to mold and fungi growth. Flexible ducts, while easier to install in tricky spaces, are generally used for shorter runs due to their higher resistance to airflow compared to rigid ducts.
Functions of Air Ducts
- Distribution of Air: The primary function of air ducts is to convey conditioned air (either heated or cooled) from the HVAC unit to various rooms or zones within a building. This ensures that spaces receive adequate airflow to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
- Maintaining Air Quality: Ductwork can also play a role in the filtration and cleaning process of the HVAC system. Air filters are often located where the air is drawn into the system, helping remove dust, pollen, and other particulates before the air is circulated throughout the building.
- Energy Efficiency: Properly designed and well-maintained ductwork is crucial for energy efficiency. Leaky or poorly insulated ducts can significantly increase energy consumption and costs by allowing heat exchange with unconditioned spaces and reducing the overall efficiency of the HVAC system.
Installation and Maintenance
The installation of air ducts requires careful planning and consideration to optimize airflow and minimize inefficiencies. Ducts should be sealed properly and insulated, particularly when they pass through unconditioned spaces like attics or crawl spaces, to prevent energy loss.
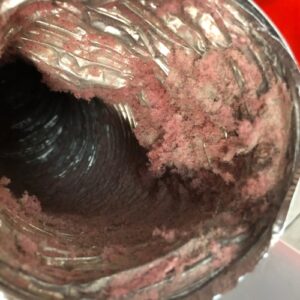
Regular maintenance, including inspection, cleaning, and repair, is essential to ensure that air ducts function properly. Over time, ducts may become clogged with dust, pet dander, and other debris, which can reduce airflow and degrade air quality. In some cases, ducts may also develop leaks that need to be sealed to prevent loss of conditioned air and increased energy bills.

What are Air Vents?
Air vents, often referred to as registers or grilles, are the components in a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system through which air is delivered to or extracted from indoor spaces. These are the visible parts of the HVAC system that allow air to move in and out of the rooms, playing a crucial role in controlling and directing the flow of air. Here’s a detailed look at air vents and their functions:
Types and Materials
Air vents come in various types and designs, each suited for specific applications within the HVAC system:
- Supply Vents: These vents are responsible for delivering conditioned air to a room. They are usually located on walls, floors, or ceilings and can be identified by the outward flow of air.
- Return Vents: Larger than supply vents, return vents pull air from indoor spaces back to the HVAC system for reconditioning and filtration. They are typically found on walls or in ceilings and are crucial for maintaining proper air circulation.
The materials used for air vents include metal (such as aluminum or steel), plastic, and sometimes wood, depending on aesthetic preferences and specific airflow requirements.
Functionality
Air vents serve several key functions within an HVAC system:
- Air Delivery and Exhaust: The primary function of air vents is to facilitate the movement of air. Supply vents distribute conditioned air throughout the building, while return vents help recycle the air back to the HVAC system.
- Airflow Control: Many air vents are equipped with adjustable louvers that allow the user to direct and control the volume of air flowing into a room. This adjustability helps manage comfort levels by directing air away from or toward occupants.
- Aesthetic Integration: Vents are designed to blend with the interior decor. Available in various styles and finishes, they can complement the aesthetic of any room without being obtrusive.
Maintenance
Maintaining air vents is relatively simple but important for ensuring effective air circulation and system efficiency:
- Regular Cleaning: Vents can accumulate dust, pet hair, and other debris, which can obstruct airflow and degrade air quality. Regular vacuuming or wiping down of vents can prevent these issues.
- Inspection for Blockages: It’s important to ensure that furniture, curtains, or other objects do not block vents. Obstructed vents can lead to inefficient system operation and uneven heating or cooling.
- Adjustment for Comfort: Adjusting the louvers to change the airflow direction can enhance room comfort, allowing for customized heating or cooling distributions based on personal preference or room usage.

Differences Between Air Ducts and Air Vents
1. Functionality and Role in HVAC System
Air Ducts:
- Main Conduits: Air ducts are the transportation highways for air within the HVAC system. They carry air from the central unit to various parts of the building and back again.
- Mistake to Avoid: Not scheduling regular maintenance checks can lead to neglected air duct issues such as leaks or blockages, which can severely affect system efficiency and air quality.
Air Vents:
- Point of Air Delivery and Return: Vents are the interface between the air duct system and the room. They control the delivery of air into the space and facilitate its return.
- Mistake to Avoid: Blocking vents with furniture or curtains is a common mistake that can restrict airflow, leading to inefficient heating and cooling and increased energy costs.
2. Visibility and Accessibility
Air Ducts:
- Hidden from View: Air ducts are typically concealed within walls, ceilings, or floors, making them less accessible.
- Mistake to Avoid: Ignoring the hidden nature of ducts can lead to prolonged undetected damage, such as mold growth or pest infestations, which can cause long-term issues within the ductwork.
Air Vents:
- Easily Accessible and Visible: Vents are located at strategic points within a room, usually where the ceiling meets the walls or on the floor, making them easily accessible and part of the room’s aesthetic.
- Mistake to Avoid: Failing to clean vents regularly can lead to dust and allergen build-up, which can decrease air quality and the overall healthiness of the indoor environment.
3. Material and Design Variability
Air Ducts:
- Durable Materials: Made from materials like galvanized steel, aluminum, or flexible plastic, designed to withstand air pressure and minimize leakage.
- Mistake to Avoid: Using improper materials or faulty installation can lead to inefficient air distribution and higher utility costs.
Air Vents:
- Variety of Materials and Styles: Vents can be crafted from various materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, allowing them to blend with or enhance the decor of a room.
- Mistake to Avoid: Choosing vents purely based on aesthetics without considering their functionality can lead to inadequate airflow and discomfort in certain areas of the building.
By understanding these distinctions and the common mistakes associated with each component, you can ensure a more efficient and effective HVAC system that better maintains temperature control, enhances indoor air quality and reduces unnecessary energy expenditure.
Age and deterioration
Age and deterioration are critical factors that can significantly impact the efficiency and functionality of air ducts within an HVAC system. Understanding how these factors affect ductwork can help homeowners and building managers make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, or replacements. Here’s a closer look at how age and deterioration affect air ducts and what can be done about it.
Impact of Age on Air Ducts
As air ducts age, they are subjected to various stresses that can lead to wear and tear. These stresses include:
- Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Constant heating and cooling cycles cause the materials of the ducts to expand and contract. Over time, this can lead to fatigue in the materials, causing cracks or separations at the joints.
- Corrosion: Metal ducts, especially those in humid or damp environments, can corrode over time. Corrosion weakens the duct structure, leading to leaks and compromised air quality.
- Material Degradation: Ductwork materials like fiberglass can degrade over time, releasing particles into the air stream. This not only affects air quality but can also decrease the insulation properties of the ducts, leading to increased energy costs.
Signs of Deterioration
The signs of aging and deterioration in air ducts can often go unnoticed until they become serious. Here are some indicators to watch for:
- Increased Energy Bills: Leaky or inefficient ductwork can cause your HVAC system to work harder, which in turn increases energy consumption.
- Uneven Heating or Cooling: If some rooms are less comfortable than others, deteriorating ductwork might be the issue, as leaks can prevent proper air distribution.
- “Musty or Moldy Smells**: Older ducts, especially those that are damp or leaky, can harbor mold and mildew, leading to unpleasant odors emanating from the vents.
- Visible Rust or Dust: Any visible signs of rust or excessive dust can indicate that the integrity of the ductwork is compromised.
Maintenance and Repair
Regular maintenance is key to extending the life of your air ducts and ensuring they operate efficiently:
- Regular Inspections: Have a professional inspect your ductwork annually. They can identify any early signs of wear and take corrective actions before significant problems arise.
- Sealing and Insulating Ducts: Properly sealing leaks and insulating ducts can greatly improve their efficiency and durability. This not only conserves energy but also reduces the strain on your HVAC system.
- Cleaning: Occasionally, ducts may need to be cleaned to remove dust buildup, mold, and other contaminants that can cause deterioration and affect indoor air quality.
Replacement Considerations
There comes a point when it may be more cost-effective to replace old and severely deteriorated ductwork rather than continuing to repair it. Consider replacement if:
- Ductwork is Over 15 Years Old: Older systems are likely less efficient and more prone to problems.
- Extensive Damage: If a significant portion of the ductwork shows signs of corrosion or leakage, replacing it might be more economical in the long run.
- Renovation or System Upgrade: If you are upgrading your HVAC system or renovating your property, it might be an opportune time to replace old ductwork to match the new system’s requirements.
Rodents and air ducts
Rodents and air ducts have a troubling relationship that can cause significant damage to HVAC systems and create health hazards within a building. Understanding the nature of this relationship and taking proactive steps to address it is crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of your air ducts. Here’s a detailed look at the issues caused by rodents in air ducts and how to effectively manage them.
How Rodents Access Air Ducts
Rodents are adept climbers and can squeeze through tiny openings, making air duct systems particularly vulnerable to infestation. Here are common ways rodents enter air ducts:
- Structural Gaps and Weaknesses: Holes as small as a dime are enough for mice to enter, and larger openings for rats. These can be due to construction gaps, deteriorating seals, or damage from other pests.
- Vents and Openings: Exhaust vents, outdoor HVAC unit connections, and uncapped chimneys provide easy access unless properly sealed.
- Connected Networks: Rodents can travel between properties in dense urban or suburban settings via connected networks like utility lines, shared basements, and common ductwork.
Problems Caused by Rodents in Air Duffts
The presence of rodents in air ducts can lead to various issues, affecting both the health of the occupants and the integrity of the HVAC system:
- Air Quality Degradation: Rodent droppings, urine, and dander can become airborne through the duct system, exacerbating allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions.
- Physical Damage: Rodents have strong teeth that can chew through ductwork materials, including flexible plastic and fiberglass, leading to leaks that compromise system efficiency.
- Odor Problems: The smell from rodent waste and, in worse cases, decaying carcasses can permeate through the vent system, creating unpleasant and persistent odors.
- Spread of Disease: Rodents are carriers of diseases such as hantavirus, leptospirosis, and salmonellosis, which can be spread through their droppings and urine.
Preventive Measures and Solutions
Taking proactive steps to prevent rodent infestations in air ducts is essential. Here are effective strategies:
- Seal Entry Points: Conduct a thorough inspection of your home and seal all potential entry points to ducts using rodent-proof materials like metal mesh or steel wool combined with caulking.
- Regular Inspections: Have your HVAC system and ductwork regularly inspected by professionals to identify and rectify potential vulnerabilities or early signs of infestation.
- Proper Ventilation Covering: Ensure that all external vents are covered with robust grilles that cannot be penetrated by rodents.
- Sanitation and Housekeeping: Reduce the attraction for rodents by keeping your property clean and free of food debris. Secure garbage in sealed containers and manage vegetation around the building foundation to discourage nesting.
Addressing an Infestation
If rodents have already infiltrated your air ducts, a strategic approach is required to eliminate them and mitigate the damage:
- Professional Pest Control: Engage a licensed pest control professional to safely and effectively remove the rodents from your property.
- Cleaning and Repairing Ductwork: After eradication, have your ductwork professionally cleaned to remove all traces of rodent presence, repair any damage, and sanitize the system to prevent health risks.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Implement a monitoring strategy to quickly detect any new rodent activity and prevent future infestations.
Breathing Easy: Understanding the Key Differences Between Air Ducts and Air Vents with The AC Therapist
As The AC Therapist, I’m here to ensure that every aspect of your HVAC system is working seamlessly to provide you with the comfort and air quality you deserve. Today, we’ve explored the vital differences between air ducts and air vents—two crucial components that might seem similar but play very distinct roles in your home’s air conditioning and heating system.
Air ducts are the hidden pathways that deliver and retrieve air throughout your home, ensuring that every room remains at your desired temperature. On the other hand, air vents are the points of contact where you interact with your HVAC system, controlling and directing the air as it enters your living spaces. Recognizing these differences can help you better understand how your HVAC system works and why each component is crucial for maintaining an efficient and healthy home environment.
Remember, regular maintenance of both ducts and vents is essential to prolong the life of your system and enhance its performance. If you ever notice issues like uneven heating or cooling, strange noises, or decreased air quality, don’t hesitate to call me, your trusted AC Therapist. Together, we can diagnose the issue and ensure that your HVAC system is in top shape, keeping your home comfortable year-round. Thank you for trusting me with your air conditioning needs. Here’s to a healthier, more comfortable home environment for all!